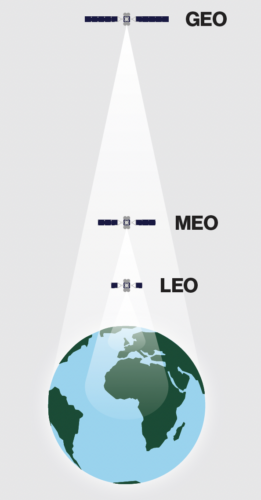
Most constellations consist of Geostationary Earth Orbit (GEO) satellites. GEO satellites move in sync with Earth’s rotation, allowing them to appear stationary. Positioned at an altitude of 35,786 kilometres, GEO satellites cover vast areas, requiring only three equally spaced satellites to offer almost global coverage. These satellites typically have a lifespan of approximately 15 years. On the other hand, Low Earth Orbit (LEO) constellations are formed by hundreds of satellites orbiting the Earth. With over 600 individual LEO satellites and numerous ground stations worldwide, LEO satellites are smaller, lighter, more cost-effective to launch, and easier to replace.
Middle Earth Orbit (MEO) constellations are, as the name indicates it, in between GEO and LEO. The altitude can vary from 5,000 to 20,000 km. LEO and GEO satellite networks are complementary, not competitive. Each can provide connectivity, with some degrees of difference in coverage and latency. Combined, they increase the capacity, reliability, and speed of connectivity bringing airlines, and passengers, truly global coverage in-flight.